Journal : The American Journal of the Medical Sciences ; vol. xcviii.
Philadelphia : Lea Brothers & Co., 1889.
Description : 248-254 p. ; ill.: 2 photos. in-text ; 24 cm.
Photographs : 2 photographic figures in-text (process unverified).
Subject : Corticobulbar tract — Inflammation ; Ophthalmoplegia.
Notes :
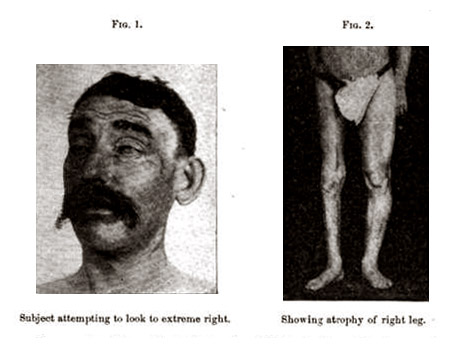
The case which I report here proves rather conclusively that the same pathological process may give rise to a typical polioencephalitis superior and to chronic or subacute poliomyelitis anterior. — Page 249.
It will hardly be necessary in this paper to prove the diagnosis of subacute poliomyelitis in this case, and considering the rarity of poliomyelitis in the adult it would be strange indeed if the occurrence of such an affection in the course of a polioencephalitis superior were a mere coincidence. It seems to me to prove positively that the ganglion cells of the anterior horns of the spinal cord are subject to the same pathological changes as the large nuclear cells on the floor of the third and fourth ventricles. — Page 252.

A clinical report which argues the differential diagnosis of ophthalmoplegia in an acquired neurodegenerative disease other than Wernicke encephalopathy or neurosyphilis. Sachs speculates that his patient is presenting with symptoms of both polioencephalitis and subacute poliomyelitis, but admits that without an autopsy it is impossible to know the location or cause of the lesions which brought on the curious multiple syndromes in this 40 year-old nontabetic patient.